The Ultimate Guide to Building a Cost-Effective Open-Source MLOps Stack in 2025
I. Introduction: The Startup MLOps Dilemma 🚀
Machine learning (ML) is no longer reserved for tech giants. From personalized marketing to predictive maintenance, ML is transforming industries across the board 🌐. As the demand for AI-driven solutions grows, even the smallest startups are feeling the pressure to integrate machine learning into their products and operations.
However, building an ML infrastructure isn’t trivial—especially for startups. With tight budgets, lean teams, and fast product cycles, many early-stage companies face a dilemma: how to build a robust and scalable MLOps pipeline without draining resources or resorting to expensive enterprise tools 💸.
That’s where open-source shines 🌟. Open-source tools offer a unique opportunity for startups to leverage battle-tested, community-supported frameworks without licensing costs. While they often require more setup and integration, they provide unmatched flexibility, transparency, and long-term cost savings. Tools like DVC, MLflow, and Prefect empower teams to version data, track experiments, and orchestrate workflows with minimal upfront investment.
This guide is designed to help you navigate the MLOps jungle by providing a tool-by-tool breakdown of the open-source stack that works best for startups in 2025. Each tool recommendation includes budget-friendly alternatives, trade-offs, and integration insights, linking to detailed, in-depth articles for hands-on implementation 📚.
Our primary audience? 👥 Technical founders, ML engineers, and DevOps professionals at early-stage startups—especially those without dedicated MLOps teams. If you’re building or scaling ML capabilities from scratch, this guide will act as your go-to reference.
Before we dive in, let’s clarify what MLOps means. MLOps, or Machine Learning Operations, refers to the practices, tools, and workflows used to deploy, monitor, and manage machine learning models in production. It bridges the gap between data science and engineering, ensuring that ML models deliver value reliably and repeatably.
📌 Bookmark this guide now—whether you’re just getting started or revisiting your stack, this article is the foundation of your open-source MLOps journey.
🔧 Recommended: For hands-on, project-based learning in MLOps, we highly recommend the Machine Learning Engineer Nanodegree by Udacity. This course covers real-world MLOps workflows, CI/CD practices, and deployment techniques used by top startups. Anchoring your team’s knowledge here could save you hundreds of engineering hours later on.
Berikut adalah paragraf-paragraf lengkap untuk bagian:
II. The MLOps Lifecycle for Startups 🔁
Building a machine learning system doesn’t end once the model is trained. Training is just the beginning. The real value of ML lies in its ability to operationalize models—that is, to move them from notebooks into production, monitor their performance, and continuously improve them based on real-world feedback.
A complete MLOps lifecycle includes the following core stages, each of which plays a critical role in enabling reliable, repeatable, and scalable ML systems:
📥 1. Data Ingestion & Versioning
Collecting, cleaning, and managing datasets is the foundation of every ML workflow. For startups, ensuring reproducibility without expensive infrastructure means using tools like DVC or lakeFS, which enable Git-like versioning for data and models.
🔬 2. Experiment Tracking
Once data is ready, models must be trained, tuned, and evaluated across experiments. Tools like MLflow and Weights & Biases help track metrics, parameters, and artifacts, making it easy to compare results and avoid costly guesswork.
🔄 3. Workflow Orchestration
To automate multi-step ML pipelines—encompassing data preprocessing, model training, evaluation, and deployment—startups often turn to orchestrators like Prefect or Apache Airflow. These tools manage dependencies, retries, and scheduling, so engineers don’t need to manually babysit scripts.
🚀 4. Model Deployment
Getting models into production means packaging them as microservices, ready to serve predictions via API. Lightweight frameworks like BentoML or Seldon Core help teams deploy models with minimal overhead, making them ideal for teams without full-time DevOps support.
📊 5. Model Monitoring
ML models can drift over time due to changing data patterns. That’s why startups must monitor model accuracy, latency, and input distributions. Tools like Evidently AI and Prometheus, combined with Grafana, help catch these shifts early and ensure your model remains reliable in production.
🔧 6. CI/CD Automation
To avoid manual deployment and testing, machine learning workflows benefit from CI/CD pipelines, just like traditional software development. With tools like CML and GitHub Actions, you can automate everything from data validation to model rollout with each pull request.
🆚 Startups vs. Enterprises: A Different Game
While enterprises often have entire teams dedicated to each MLOps stage, startups must prioritize speed, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. Instead of building robust, multi-layered platforms, early-stage teams should embrace Minimum Viable MLOps (mvMLOps)—a lean, modular approach that scales with the company.
For example, while a large company might invest in custom Kubernetes clusters and ML platforms like AWS SageMaker, a startup can achieve 80% of the value with open-source tools and clever integrations—at a fraction of the cost. 💡
🗺️ the MLOps Lifecycle
To make things concrete, here’s a visual overview of the startup MLOps lifecycle:
Data Ingestion → Versioning → Experimentation → Orchestration → Deployment → Monitoring → CI/CD
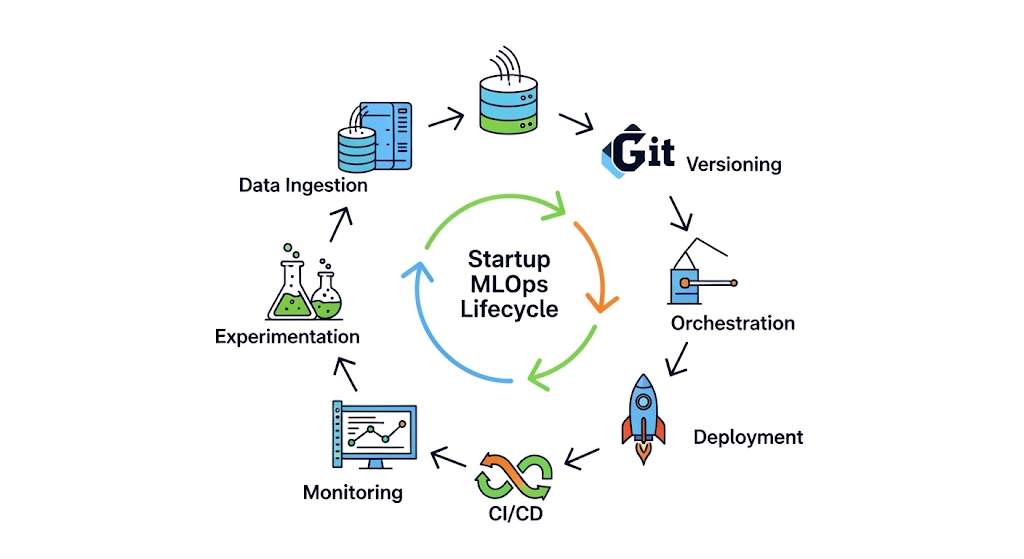
Each stage is modular, meaning you can start small and plug in tools as needed—without committing to a complete platform upfront.
✅ Recommended: Want to explore this lifecycle hands-on? Check out the ML Engineering for Production (MLOps) Specialization by DeepLearning.AI on Coursera. Created by Andrew Ng and his team, it’s one of the most authoritative MLOps courses for professionals and startups alike.
III.A. Data & Model Versioning 🧬
In the world of machine learning, data is as important as code—if not more. However, while developers have long benefited from tools like Git for code versioning, data versioning introduces unique challenges, including large file sizes, binary formats, and evolving datasets. For startups, where reproducibility and collaboration are critical (but resources are limited), finding the right data versioning strategy can mean the difference between chaos and clarity. ⚖️
🏆 Primary Tool: DVC (Data Version Control)
DVC is the gold standard for open-source data versioning. Built to bring Git-like workflows to data and ML models, DVC enables teams to track data, manage model files, and share experiments—all within your Git repo. With support for remote storage (such as AWS S3, Google Cloud, or SSH), DVC makes collaboration across teams seamless without increasing your repository size.
Key benefits of DVC include:
- Versioning datasets alongside code 🗃️
- Sharing ML experiments with .dvc metafiles 🔄
- Plug-and-play integration with CI/CD workflows and pipelines 🛠️
Its tight integration with Git makes it ideal for small, fast-moving teams who already live in version control systems.
💡 Alternative: Git LFS (Large File Storage)
If you’re looking for a straightforward approach or are just starting, Git LFS can be a lightweight solution. It extends Git’s capabilities by tracking large files, such as datasets and model weights. However, Git LFS lacks the ML-specific functionalities (such as pipeline stages and parameter tracking) that DVC offers. Additionally, free Git LFS storage is limited on platforms like GitHub, which may introduce hidden costs as your data grows 📈.
Use Git LFS if:
- You’re managing a few large binary files 📁
- Your team already uses GitHub and wants minimal setup 🚀
🧪 Bonus Tool: lakeFS
Another emerging option is lakeFS, which brings Git-like version control directly to object stores like S3. This is particularly powerful for data lakes and big data pipelines. lakeFS supports atomic commits, branching, and rollback across terabyte-scale datasets—ideal for data engineering-heavy startups.
Note: lakeFS works best in data lake architectures and may be overkill for teams with modest storage needs or without cloud-native infrastructure.
🔗 Integration Tips
- Combine DVC + CML (Continuous Machine Learning) to create end-to-end, GitOps-driven pipelines.
- Use DVC remotes (such as Google Drive, S3, or Azure Blob Storage) to offload storage costs while maintaining tight version control.
- If using GitHub Actions, DVC integrates directly into your workflow via simple commands in your .yaml pipeline.
📚 Deep Dive: Data & Model Versioning on a Budget: A Deep Dive into DVC vs. Git LFS vs. lakeFS
In our dedicated related article, we break down real-world scenarios, performance benchmarks, and configuration tips to help you select the right tool based on team size, data volume, and future scalability needs.
🧰 Recommended: If you’re just starting with data engineering or ML pipelines, the Data Version Control for Machine Learning Projects course on DataCamp offers a hands-on, beginner-friendly introduction to DVC. It’s a great way to upskill yourself or your team before committing to a full-stack rollout.
Berikut adalah paragraf-paragraf lengkap untuk bagian:
III.B. Experiment Tracking 📊
In any machine learning project, tracking experiments is critical to success. Without a system for managing and comparing models, parameters, metrics, and artifacts, you’re flying blind ✈️. Especially for startups that iterate rapidly, it’s easy to lose track of what works, what doesn’t, and why. This is where experiment tracking tools shine—bringing structure, visibility, and reproducibility to your ML workflows.
🏆 Primary Tool: MLflow
MLflow is an open-source platform for managing the ML lifecycle, and it has become the de facto standard in many open-source stacks. It offers a simple yet powerful interface for logging experiments, visualizing metrics, managing model artifacts, and even packaging models for deployment. Best of all, it’s self-hostable and integrates seamlessly with Python scripts, Jupyter notebooks, and popular ML frameworks like Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch 🧪.
Startups love MLflow for its:
- No-vendor lock-in approach 🔓
- Ability to scale from local experimentation to a production-ready model registry
- Native support for REST APIs and integration with tools like DVC and Docker
For small teams that want complete control over their infrastructure without compromising on features, MLflow strikes the sweet spot.
💻 Alternative: Weights & Biases (Free Tier)
Weights & Biases (W&B) provides a more polished and collaborative experience, particularly if your team is remote or prefers working in the cloud. It provides real-time visual dashboards, hyperparameter sweeps, media logging, and tight integration with popular ML libraries. The Free Tier includes unlimited public projects and a generous quota for private ones, making it very appealing for early-stage startups.
Use W&B if:
- You want plug-and-play functionality with zero infrastructure setup ☁️
- You value a beautiful, shareable UI for experiment results 🖼️
- Your team collaborates across time zones and needs central visibility 🌍
Please note that once your team outgrows the free tier or requires advanced features such as artifact versioning or audit trails, you’ll need to upgrade to the Pro plan.
🧭 Alternative: Neptune.ai (Free Tier)
Neptune.ai offers a hybrid approach, serving as both a metadata store and an experiment tracker, with strong support for custom workflows. While its UI is less flashy than W&B, it provides excellent flexibility, especially for teams with unique logging requirements. The free tier includes 100 GB of storage and unlimited team members, making it ideal for collaboration without requiring upfront payment.
Use Neptune.ai if:
- You need fine-grained control over metadata logging ⚙️
- You want to separate logging from your ML framework logic.
- You prioritize clean, structured experiment histories for audits or compliance 🧾
💰 Cost-Benefit Analysis for Startups
| Tool | Free Tier | Hosting | Best For |
| MLflow | ✅ | Self-hosted | Full control, customization, offline use 🧩 |
| Weights & Biases | ✅ | Cloud | Collaboration, visualization, ease-of-use 🎯 |
| Neptune.ai | ✅ | Cloud | Flexibility, metadata tracking, clean audit trails 📋 |
Each tool provides essential experiment tracking features, but your choice should align with your team’s infrastructure, collaboration needs, and growth plans. If you need to iterate fast without worrying about servers, W&B or Neptune are excellent out-of-the-box options. If you want full-stack control and long-term flexibility, MLflow is the ideal choice.
📚 Deep Dive: Lean Experiment Tracking: MLflow vs. Weights & Biases (Free Tier) vs. Neptune.ai (Free Tier)
In this dedicated related article, we provide code examples, performance benchmarks, and real-world use cases to help you decide which tracker fits your startup best. Whether you prioritize self-hosting, team dashboards, or audit-ready logs—we’ve got you covered.
🧰 Recommended: Want to get hands-on with real-world experiment tracking and ML workflows? Try the Comet ML for Teams platform—used by companies like Zappos and Ancestry.com. While Comet isn’t open source, its free tier supports up to three team members. It offers powerful features, such as model comparison dashboards and auto-logging—a great companion for fast-moving teams experimenting with multiple tools.
Berikut adalah paragraf-paragraf lengkap untuk bagian:
III.C. Workflow Orchestration 🔄
Once your experiments are repeatable, it’s time to automate them—and that’s where workflow orchestration comes into play. Orchestration tools enable you to schedule, monitor, and manage multi-step machine learning pipelines. For startups aiming to build production-grade ML systems with small teams, a good orchestrator ensures consistency, visibility, and scalability without getting overwhelmed by complexity 🛠️.
🏆 Primary Tool: Prefect
Prefect has quickly become a favorite in the open-source community for its Python-native, modern approach to orchestration. Designed with developer experience in mind, Prefect allows you to build data and ML workflows using regular Python functions—no need to learn a DSL or complex configurations 🙌.
Key advantages of Prefect:
- Easy-to-write workflows using Python decorators 🐍
- Rich UI for visualizing and debugging runs 🖥️
- Native support for async tasks, retries, schedules, and caching
- Option to self-host (open-source) or upgrade to Prefect Cloud for a managed backend
Prefect is ideal for startups that want fast iteration cycles, full control, and minimal infrastructure overhead. Its intuitive developer experience makes onboarding new team members much easier than legacy platforms.
⚙️ Alternative: Apache Airflow
Apache Airflow is the industry standard for data orchestration, widely used by large enterprises and data engineering teams. It offers robust DAG scheduling, task dependency management, and extensive plugin support. However, Airflow’s learning curve and maintenance overhead can be a challenge for lean teams.
Use Airflow if:
- You need high reliability and complex scheduling (e.g., cron-based workflows) 🕒
- Your workflows are heavily tied to batch processing and ETL pipelines 📦
- Your engineers are already familiar with DevOps tools and infrastructure.
Keep in mind that setting up and maintaining Airflow often requires Kubernetes or Docker Swarm, as well as dedicated monitoring tools such as Prometheus and Grafana.
🤖 Alternative: Kubeflow Pipelines
Kubeflow Pipelines is purpose-built for ML workflows in Kubernetes environments. It’s highly extensible and integrates tightly with the rest of the Kubeflow ecosystem—including model training, serving, and monitoring. However, the setup is Kubernetes-dependent, making it more suitable for startups with a higher level of DevOps maturity.
Use Kubeflow Pipelines if:
- You’re already deploying models with Kubernetes 🧱
- You need native support for TensorFlow Extended (TFX) or Argo Workflows.
- You have an in-house MLOps or platform engineering team.
🧠 Decision Criteria: How to Choose the Right Orchestrator
| Criteria | Prefect ✅ | Airflow ⚙️ | Kubeflow Pipelines 🤖 |
| Language | Python-native 🐍 | Python + YAML | Python + Kubernetes SDK |
| Ease of Use | High 💡 | Moderate | Low (complex infra) |
| Best For | ML startups & workflows | ETL, BI, batch jobs | Kubernetes-based ML pipelines |
| Hosting Options | Cloud & open-source 🌐 | Self-hosted only | Self-hosted (K8s required) |
| Visualization | Clean modern UI 🖼️ | Basic (can integrate) | Advanced, Kubernetes-native |
For most startups, Prefect offers the best balance of power, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. It gets you from prototype to production with minimal setup—and scales with your team.
🧰 Diagram: A Typical ML Workflow DAG
Here’s a simple DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) illustrating a typical machine learning pipeline:
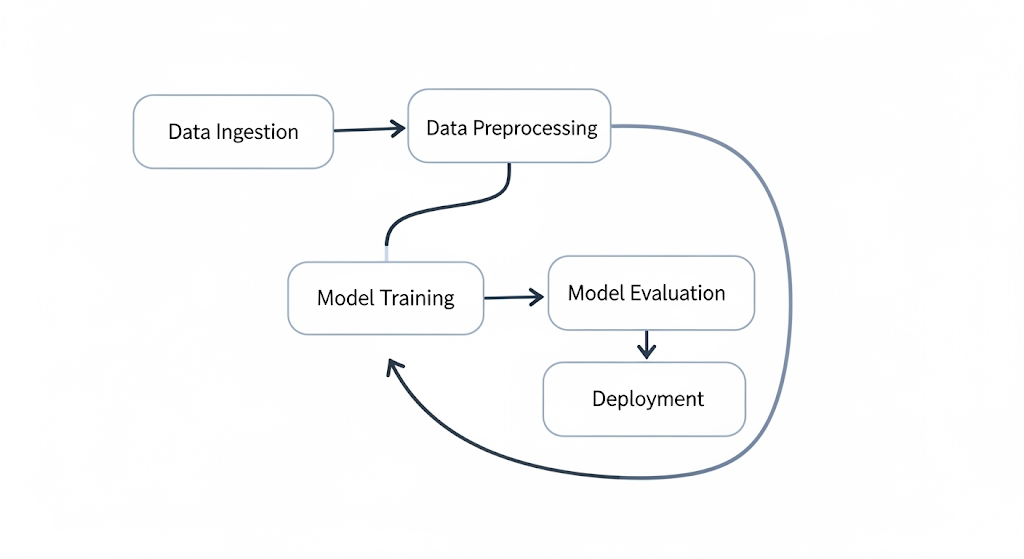
Each task in this pipeline can be triggered on a schedule, retried if it fails, and logged for monitoring—all using a workflow orchestrator like Prefect or Airflow.
📚 Deep Dive: Choosing Your Orchestrator: A Startup’s Guide to Airflow vs. Kubeflow Pipelines vs. Prefect
In our related article, we provide real deployment examples, YAML snippets, cost comparisons, and setup walkthroughs to help you choose and configure the right orchestrator based on your current stack and team skills.
🎓 Recommended Product: Want hands-on training in building production-ready ML pipelines with orchestration? We recommend the Data Pipelines with Prefect Course on Udemy. It’s beginner-friendly, up-to-date with Prefect 2.0, and perfect for small teams looking to implement orchestration quickly and effectively.
III.D. Model Serving 🚀
After training your model and tracking experiments, the next challenge is getting your model into production—in a way that’s fast, reliable, and scalable. This step, known as model serving, involves packaging your trained models as APIs or services, allowing applications, users, or other systems to interact with them in real-time or batch mode. For startups, choosing the proper serving framework can significantly reduce operational overhead and time-to-market.
🏆 Primary Tool: BentoML
BentoML is an open-source framework that simplifies model packaging and deployment into REST or gRPC APIs. It supports multiple frameworks (PyTorch, TensorFlow, XGBoost, Scikit-learn, and more), allowing you to serve models as microservices with just a few lines of code ⚡.
Key features:
- REST & gRPC interface generation out of the box 🌐
- Built-in support for Docker containerization 🐳
- Integration with Yatai for model registry and deployment tracking
- Easy cloud-native deployment on AWS, GCP, or on-prem via Kubernetes ☁️
BentoML is ideal for lean teams that want a developer-first model serving solution without having to build their container infrastructure from scratch. It’s highly scriptable, making it perfect for rapid prototyping and productionizing models in agile environments.
⚙️ Alternative: Seldon Core
Seldon Core is a powerful, Kubernetes-native model serving platform designed for more complex and large-scale deployments. It supports advanced routing, A/B testing, canary releases, and integrates tightly with monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana 📊.
Use Seldon Core if:
- Your team is already using Kubernetes to manage infrastructure 🧱
- You require advanced production patterns like shadow deployments or multi-model routing 🔄
- You’re working in regulated environments that need observability and governance.
However, Seldon comes with a steeper learning curve and requires Kubernetes expertise—something that early-stage startups may find overkill.
🧪 Serving Strategies: REST, gRPC, and Batch
When deciding how to expose your model, consider the following serving strategies:
- REST APIs: Simple to implement and integrate with most frontend and backend systems. Great for web-based apps or services needing synchronous inference 📲.
- gRPC: Faster and more efficient than REST for internal microservices. Ideal for high-throughput, low-latency systems 💨.
- Batch Serving: Preferred when dealing with large datasets that don’t require real-time inference. Often used for overnight scoring jobs or ETL workflows 🗂️.
Both BentoML and Seldon support REST and gRPC interfaces; however, batch serving typically requires custom orchestration, often built on top of tools such as Prefect or Airflow.
🐳 Docker & Kubernetes Integrations
Model serving at scale benefits tremendously from containerization. Both BentoML and Seldon provide native support for Docker, allowing your model services to be encapsulated and deployed reproducibly across environments.
- With BentoML, creating a Docker container is as simple as bentoml containerize.
- With Seldon, your models are deployed as Kubernetes pods, managed through custom CRDs (Custom Resource Definitions).
For startups without DevOps engineers, BentoML offers the faster path to production, while Seldon is better suited for teams already investing in Kubernetes-based workflows.
📚 Deep Dive: Deploying Models without Breaking the Bank: A Practical Guide to Seldon Core vs. BentoML
In the corresponding related article, we compare deployment time, scalability, and real-world infrastructure costs for each tool. Whether you’re serving a single model on AWS or dozens in a hybrid-cloud setup, we walk you through it—step by step.
🎓 Recommended: Want a structured way to learn model deployment and Kubernetes at the same time? Enroll in “Deploying Machine Learning Models in Production with Kubernetes” on Coursera. It’s hands-on, beginner-friendly, and offers a real-world perspective on container-based ML deployments—ideal for founders and engineers building scalable ML apps.
III.E. Model Monitoring 🔍
Deploying a machine learning model is just the beginning—keeping it healthy in production is where real challenges begin. Over time, models can degrade due to changes in incoming data (data drift), shifts in user behavior (concept drift), or infrastructure issues that impact latency and availability. For startups, monitoring models isn’t a luxury—it’s a mission-critical necessity that helps avoid silent failures and wasted compute costs ⚠️.
🏆 Primary Tool: Evidently AI
AI is a purpose-built open-source tool that focuses on monitoring machine learning models—specifically for data and concept drift, target leakage, missing values, and feature distribution shifts 📉. What makes it unique is that it’s designed for ML from the ground up, meaning it understands the nuances of model behavior and performance in real-world pipelines.
Key advantages of Evidently:
- Out-of-the-box drift detection reports (data, target, prediction) 📊
- Web-based dashboards and Jupyter Notebook support 🧪
- Can be integrated directly into batch or real-time pipelines using Python 🐍
- Lightweight enough to run without complex infrastructure—perfect for lean teams ⚡
For startups that want visibility into why models are failing, not just whether they are, Evidently is an excellent starting point.
📈 Alternative: Prometheus + Grafana
If your startup is already using DevOps monitoring tools, combining Prometheus with Grafana provides a powerful and flexible monitoring stack. Initially designed for system metrics, Prometheus can be adapted to track ML-specific signals, such as inference latency, error rates, and resource usage (CPU, memory, GPU) 🚀.
Use this stack if:
- You’re already running Kubernetes or Dockerized services 🐳
- You want to monitor both infrastructure and models in a single dashboard 🖥️
- You have in-house ops or SRE skills capable of setting up exporters and alerts 🔧
While Prometheus + Grafana provide excellent observability, they require more configuration and do not include ML-specific diagnostics out of the box—which means you’ll have to build custom exporters and visualizations.
📏 Key Monitoring Metrics for Startups
To effectively monitor ML models, startups should prioritize the following metrics:
- Data Drift: Changes in input data distribution that impact model accuracy
- Concept Drift: Shifts in the relationship between inputs and targets over time
- Latency: Time taken for a model to return predictions—critical for real-time systems
- Prediction Confidence: Identifying low-confidence outputs or uncertainty zones
- Error Rate / Accuracy Degradation: Ongoing performance benchmarks
- Feature Nulls / Anomalies: Unexpected patterns or missing values in inputs
These metrics ensure that models remain trustworthy and cost-effective in production environments.
🖼️ Sample Dashboard (Imagined)
AI Drift Report Sample:
- X-axis: Time windows (e.g., weekly batches)
- Y-axis: Feature drift score (Kolmogorov–Smirnov metric)
- Color-coded feature importance indicators
- Highlighted alerts for sudden distribution shifts ⚠️
Prometheus + Grafana Sample:
- Line chart of model response time over time
- Bar graph of GPU usage per inference batch
- Pie chart showing the top 5 input classes for prediction volume
(For actual visuals, check Evidently’s open-source dashboard examples or Grafana’s ML monitoring templates).
📚 Deep Dive: Free & Open-Source Model Monitoring: A Practical Guide to Evidently AI with Prometheus & Grafana
In our linked article, we demonstrate how to set up monitoring pipelines, configure drift detection, create alerts, and visualize metrics using both Evidently and Prometheus-based stacks. Step-by-step setup for AWS, GCP, and local environments is included.
🎓 Recommended: For teams new to production monitoring or MLOps SRE, we recommend the “Machine Learning in Production: Monitoring and Observability” course by DeepLearning.AI. It guides you through real-world strategies for maintaining stable and observable ML models, even under changing conditions—ideal for fast-paced startup teams.
III.F. CI/CD for ML ⚙️
In modern software development, CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipelines are standard. For machine learning, the stakes are even higher—models must be retrained, validated, and deployed regularly as data changes 📈. Without automation, these tasks become prone to errors and time-consuming. That’s why building a lean, automated CI/CD pipeline is crucial for startups deploying machine learning systems at scale 🚀.
🏆 Primary Tool: CML by DVC
CML (Continuous Machine Learning) is an open-source tool created by the team behind DVC, specifically designed to bring ML workflows into CI/CD systems. It enables teams to run model training, evaluation, and reporting directly inside Git-based platforms like GitHub and GitLab 🧠.
Key benefits of CML:
- Integrates with popular CI runners like GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, and Bitbucket Pipelines
- Automatically generates and comments model performance reports in pull requests 💬
- Supports GPU-enabled runners on cloud or on-prem infrastructure
- Works natively with DVC, allowing data pipelines and model training to be versioned and reproduced ✅
For startups, CML enables a GitOps approach to ML, turning model development into a trackable, testable, and collaborative process—just like writing code.
🔁 Alternative: GitHub Actions
If you’re already using GitHub Actions for software CI/CD, it can also be extended to manage ML workflows. With proper scripting and secrets management, GitHub Actions can:
- Run model training jobs on schedule or trigger
- Validate new models against benchmarks.
- Deploy artifacts to cloud services like AWS S3 or Hugging Face.
- Integrate with tools like MLflow, Docker, and Terraform 🛠️
GitHub Actions is ideal if:
- You’re building simple ML pipelines that don’t require heavy GPUs 🧮
- You want minimal setup and tight integration with GitHub PRs and issues.
- You prefer an all-in-one CI/CD platform with robust ecosystem support.
However, for complex pipelines involving experiment tracking, datasets, and metrics, CML offers a more ML-native interface.
🧱 Sample CI/CD Pipeline: YAML Configuration Example
Here’s a simplified GitHub Actions + CML pipeline that trains a model and posts evaluation results as a comment on a pull request:
name: Train Model
on:
pull_request:
paths:
- '**.py'
- 'data/**'
- 'models/**'
jobs:
train:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: 3.10
- name: Install Dependencies
run: pip install -r requirements.txt
- name: Run Training Script
run: python train.py
- name: Post Results with CML
env:
REPO_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
run: |
echo "## 📊 Model Metrics" > report.md
python eval.py >> report.md
cml comment create report.mdThis setup allows teams to track model changes, document results, and collaborate transparently via pull requests—ideal for distributed startup teams 🌍.
🔄 MLOps + DevOps Convergence
The line between DevOps and MLOps is becoming increasingly blurred. As ML systems become more integrated into core applications, the need for consistent, automated deployment increases. CI/CD workflows not only help manage model code and dependencies but also ensure that:
- New data trigger model retraining
- Validation prevents regression in performance.
- Metrics, not just code reviews, gate deployment 🚦
Tools like CML and GitHub Actions make this convergence possible, empowering startups to implement full-lifecycle automation with limited ops resources 🧑💻.
📚 Deep Dive: Automating the CI/CD Pipeline for ML: A Practical Workflow with CML and GitHub Actions
In the linked related article, we walk through setting up GPU runners, publishing models to cloud endpoints, and automating retraining schedules—complete with templates, Terraform snippets, and best practices for scaling.
🎓 Recommended: Ready to master CI/CD for ML workflows? Check out the “MLOps with GitHub Actions and CML” course on Udemy. This beginner-to-intermediate course walks you through real-world pipelines, including experiment tracking, reporting, and multi-environment deployments—perfect for growing startup teams looking to ship faster 💥.
🎯 With CI/CD in place, your ML stack is now automated, observable, and production-ready. Next, let’s wrap it all up in our final section: Integration and Orchestration 🔗.
IV. Integration and Orchestration: Making It All Work Together 🧩
By now, we’ve explored the best open-source tools for each stage of the MLOps lifecycle—from data versioning to model deployment. But using these tools in isolation is only half the battle. The real challenge—and opportunity—is in stitching them together into a cohesive, automated system that delivers business value reliably and at scale 🛠️.
🔗 Connecting the Dots: The Integration Challenge
Most open-source tools are modular by design, which is both a strength and a complexity. Integrating DVC with MLflow, Prefect with Docker, or CML with GitHub Actions requires thoughtful planning around data flow, artifact sharing, configuration management, and execution environments.
Startups must ask:
- Where will models live?
- How will data be accessed and versioned?
- How do we ensure pipeline reproducibility across dev and prod environments?
To address this, we rely on the foundational infrastructure stack of modern MLOps, comprising Docker, Kubernetes, and Helm.
🐳 Docker, Kubernetes, and Helm: The Glue of Modern MLOps
- Docker ensures that every component—from data preprocessing to model serving—runs in a consistent, reproducible environment. It eliminates “works on my machine” issues and simplifies collaboration across teams 🚢.
- Kubernetes provides orchestration for containers, enabling the automatic scaling of services, efficient resource management, and seamless handling of failures. 🧠
- Helm simplifies the deployment of complex applications on Kubernetes by using templated configuration files called “charts” 📦.
Together, these tools allow you to package your entire ML pipeline into portable, manageable units, deployable across local, cloud, or hybrid infrastructure.
🏗️ Example Architecture Diagram
Here’s a high-level example of what an integrated MLOps stack might look like:
This architecture supports both batch and real-time workflows, offers team collaboration, and is modular enough to evolve.
👩💻 JupyterHub: A Collaborative ML Environment
JupyterHub enables multiple users to work with shared notebooks while maintaining isolation and authentication. It’s an excellent environment for:
- Running experiments and EDA (Exploratory Data Analysis) 📊
- Accessing shared datasets and logs
- Collaborating across data scientists, engineers, and product teams 🤝
For cloud-native setups, consider deploying JupyterHub on Kubernetes using Helm charts for security and scalability.
🔁 Reproducible, Portable Workflows
To ensure workflows are reproducible across environments and over time, use a combination of:
- DVC for versioning data and model artifacts 📦
- MLflow for logging experiments and registering models 🧪
- Prefect for orchestrating multi-step pipelines with retriable logic 🔁
- Dockerfiles and Docker Compose to standardize execution environments across team members.
This setup ensures that any team member—or even your CI/CD pipeline—can re-run experiments with the same inputs and dependencies 🔐.
🧰 Common Pipelines with Prefect + MLflow
For example, a typical training pipeline might look like this:
- Prefect Task 1: Load versioned data from DVC
- Prefect Task 2: Train model and log metrics to MLflow
- Prefect Task 3: Register best-performing model
- Prefect Task 4: Deploy via BentoML
- Prefect Task 5: Trigger monitoring and notify the team in Slack
Using Prefect’s task dependency graph and MLflow’s APIs, this pipeline can run on schedule or be triggered by a GitHub PR, ensuring agility and automation at once.
🔒 Security Best Practices (Because Open-Source ≠ Insecure)
Just because your stack is built on open-source doesn’t mean you can ignore security. Startups often overlook key vulnerabilities, particularly when handling sensitive data or implementing cloud-native deployments.
Best practices include:
- Use secrets management tools like HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager to avoid hardcoded credentials 🔐
- Set role-based access controls (RBAC) in Kubernetes clusters and CI/CD systems 👮
- Regularly scan Docker images using tools like Trivy to detect vulnerabilities 🛡️
- Apply network policies and firewalls to restrict exposure of internal services 🌐
For a complete checklist, refer to OWASP’s Machine Learning Security Guidelines.
🎓 Recommended: Want to master Kubernetes-based ML pipelines securely? Enroll in the “MLOps with Docker, Kubernetes, and TensorFlow” course on Udemy. It’s perfect for startups aiming to connect orchestration tools and scale securely.
In the next and final section, we’ll wrap up with a comprehensive summary table 🧾 and guide you toward actionable next steps to implement your open-source MLOps stack. Let’s bring it all together 💡.
V. Trade-Offs and Cost Considerations 💰⚖️
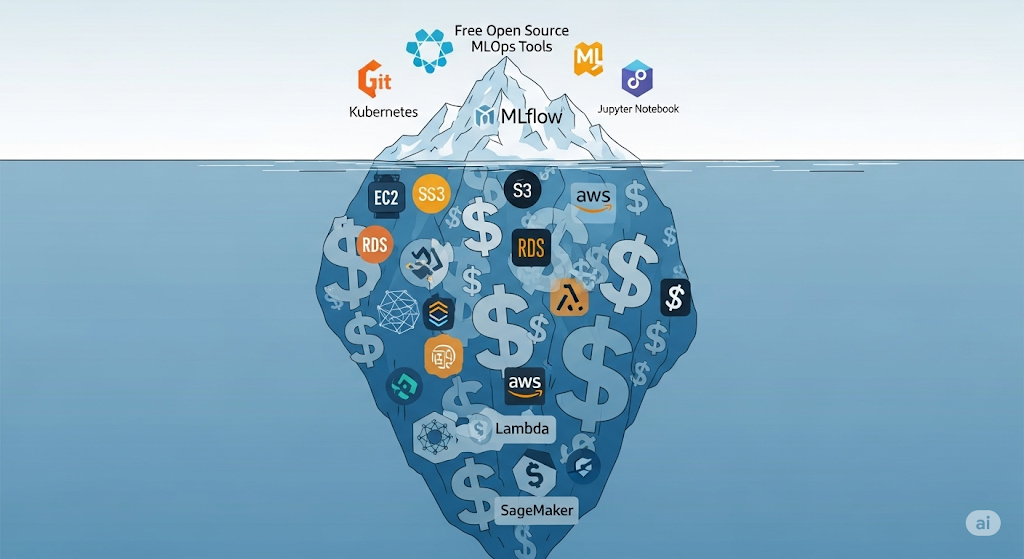
While open-source tools are often marketed as “free,” the actual cost of ownership (TCO) can quickly grow when you factor in the infrastructure, DevOps maintenance, team expertise, and scaling requirements 🧠💻. For startups especially, making the right cost-performance trade-off is critical—not just to conserve budget, but to ensure you’re building systems that are sustainable in the long term.
🧾 The Real Cost of Self-Hosting
Running your own open-source MLOps stack involves hidden costs beyond the free software license:
- Infrastructure: Hosting DVC remotes on S3, spinning up MLflow servers, running Airflow schedulers, or deploying Kubernetes clusters all incur cloud compute and storage charges 🖥️💾.
- Operational Overhead: Who maintains uptime? Who patches bugs? You’ll need DevOps or MLOps engineers (or time taken from existing developers) to manage updates, failures, and scalability.
- Learning Curve: Your team must master tool configurations, integrations, and observability to ensure seamless operation. Open-source tools often come with limited support, meaning extra hours spent on GitHub issues or Stack Overflow.
According to Forrester, the total cost of self-hosting often exceeds that of managed services by 30–50% once engineering time is factored in. That’s a big deal for a team with only 1–2 ML engineers.
🏎️ Performance vs. Complexity: Finding the Startup Sweet Spot
With open-source, you gain flexibility and modularity—but at the cost of added complexity. Want custom metrics in monitoring? Easy. Want tight integration between training and deployment? Possible. But every added feature requires:
- More infrastructure knowledge 🧱
- More testing and debugging 🧪
- More security configurations 🔐
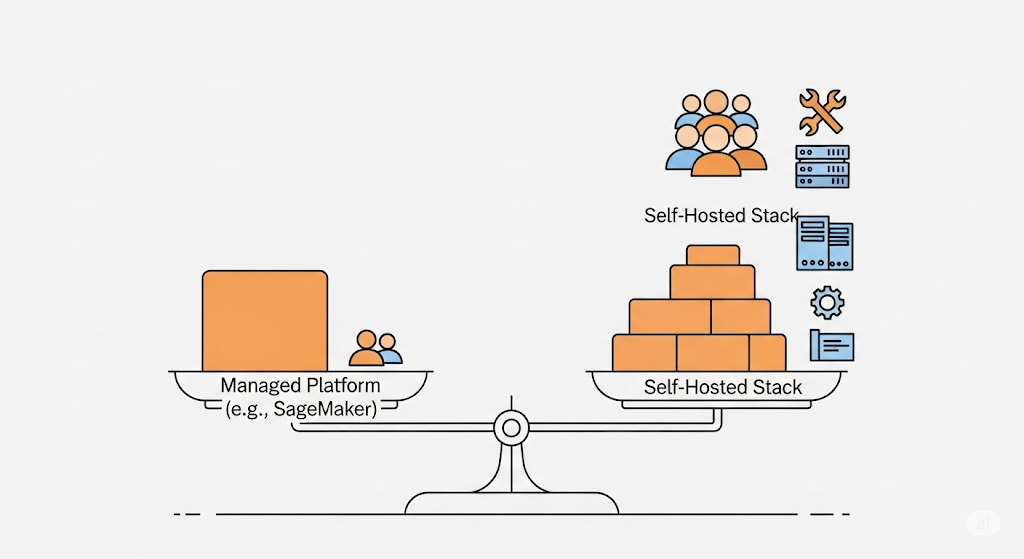
Managed services, on the other hand, often trade flexibility for speed and ease of use. However, you may encounter limitations in features or face vendor lock-in.
Startup Recommendation: Start with a minimal self-hosted stack (e.g., DVC, MLflow, and Prefect), and only scale up to more complex orchestrators or integrations as needed. Consider using managed services for non-differentiating parts of the stack, such as hosting JupyterHub or serving models with AWS Lambda.
🧠 When Managed Services May Be Worth It
Sometimes, managed platforms are not only faster to deploy—but also cheaper in the long run. Tools like AWS SageMaker, Google Vertex AI, or Azure Machine Learning offer:
- Fully integrated pipelines: data, training, serving, monitoring 🔄
- Auto-scaling infrastructure with cost controls 🌐
- Enterprise-grade security and compliance features 🛡️
- 24/7 support and managed uptime guarantees 🔧
If your team lacks MLOps capacity or needs to meet compliance or SLA targets quickly, it may be more sensible to build on top of managed platforms, at least initially.
📈 According to Gartner, hybrid MLOps adoption—mixing open-source tools with cloud-managed components—is becoming the dominant trend among high-growth startups.
📚 Deep Dives:
- The True Cost of “Free”: Analyzing Hidden Infrastructure Costs of a Self-Hosted MLOps Stack on AWS
- Is a Managed Platform (e.g., SageMaker) Ever Cheaper? A Break-Even Analysis for Startups
These linked related articles break down cost models using absolute AWS pricing, explore trade-offs such as GPU availability and regional pricing, and present decision trees to help your team make informed choices.
🎓 Recommended: Want help calculating and optimizing your startup’s infrastructure spend? Try CloudZero—a cloud cost intelligence platform built for engineering teams. It helps you track cloud costs per feature, per team, and per model in real-time, so you can identify and eliminate waste before it drains your budget 🧾📉.
In the next section, we’ll tie everything together with a comprehensive summary table 🧩—your go-to reference for building a scalable, cost-effective MLOps stack in 2025. Let’s bring it all home 🏡.
VI. Monetization and Practical Upskilling 💼📈
An open-source MLOps stack isn’t just about cutting costs—it can also be a career catalyst and a revenue opportunity for individuals and startups alike. By mastering the key tools in this ecosystem, ML engineers not only build better systems—they position themselves for premium roles, freelance contracts, and productized services in one of the fastest-growing domains in tech 🌍.
🎓 Recommended Learning Path: Udacity’s Machine Learning Engineer Nanodegree
For those looking to upskill and transition into MLOps or system-level ML engineering roles, we strongly recommend the Machine Learning Engineer Nanodegree by Udacity 📘.
This program offers:
- Hands-on projects using real-world datasets 📊
- Model deployment, CI/CD pipelines, and monitoring implementation
- Code reviews, mentorship, and career support for job placement
- Practical experience with open-source tools like MLflow, Docker, and AWS SageMaker
👉 For hands-on training, the ML Engineer Nanodegree by Udacity offers a project-based curriculum that mirrors the workflows and challenges faced in fundamental MLOps roles.
Whether you’re an early-career data scientist or a software engineer looking to pivot, this course is a strategic investment in your future in AI infrastructure.
🧰 Additional Tools to Master for Career Growth
To thrive in the MLOps space, professionals should expand beyond modeling and learn how to manage infrastructure, deployment, and APIs. Here are five high-impact tools to master:
- Docker 🐳 – For containerizing ML apps and ensuring reproducibility across environments.
- Kubernetes ☸️ – For scaling deployments, managing resources, and handling ML workloads in production.
- Terraform 📦 – To automate and version your cloud infrastructure (IaaC).
- PyTorch 🔥 – As a preferred deep learning framework for research and production.
- FastAPI ⚡ – For creating high-performance APIs to serve models in real-time.
These tools not only help build robust MLOps pipelines but also make you more competitive in interviews, freelance projects, and technical leadership roles.
💡 Monetization Opportunities for Practitioners & Teams
Mastery of MLOps tools opens the door to multiple income channels:
- Freelance/Consulting: Offer MLOps setup for early-stage startups lacking internal expertise 🤝
- Content Creation: Launch a blog, YouTube channel, or Substack around tutorials, case studies, and product reviews 🎥
- Digital Products: Sell templates, CI/CD starter kits, Helm charts, or Terraform modules on platforms like Gumroad or GitHub Sponsors 💻
- Online Courses: Create your mini-course on niche tools like DVC or Prefect using Teachable or Podia
With the proper knowledge and positioning, even solo developers can build six-figure revenue streams around MLOps infrastructure 🌱💸.
📚 Deep Dive: Building Your MLOps Career: Essential Open-Source Tools to Master for Interviews
In this dedicated related article, we share interview questions, career paths, and tool mastery checklists to help you land jobs, freelance gigs, or start your own MLOps consulting business. Whether you’re aiming for FAANG, startups, or remote independence, this guide is your launchpad.
🧠 Pro Tip: Stay updated by following industry voices like Chip Huyen, MLOps Community, and Arize AI’s webinars—they frequently share trends, tools, and real-world case studies.
In our final section, we’ll summarize everything into a quick-reference table 📋—so you can start building your stack with clarity and confidence. Let’s wrap it all up.
VII. Final Thoughts and Next Steps 🧭
Building a high-performance MLOps stack doesn’t require an enterprise budget. With the right combination of open-source tools, thoughtful orchestration, and cloud-native practices, startups can compete with industry giants—without burning through capital 💡🔥. This guide has walked you through a practical, cost-effective blueprint for designing and operating a complete machine learning lifecycle using proven technologies that are scalable, reproducible, and production-ready.
📚 Dig Deeper: Explore the Related Articles
Each component we covered—versioning, experimentation, orchestration, deployment, monitoring, CI/CD—has its complexities and trade-offs. To help you take action, we’ve created dedicated related articles that provide:
- Hands-on tutorials and sample configurations 🔧
- Detailed comparisons and performance benchmarks 📊
- Monetization tips and integration best practices 💼
👉 Head over to the related article index to explore these deep dives and accelerate your implementation process.
🚀 Kickstart Your Stack: GitHub Starter Repo
We’ve also published a starter GitHub repo with boilerplate code to help you get up and running. It includes:
- Dockerized ML pipeline examples
- CI/CD workflows using GitHub Actions and CML
- Templates for DVC, MLflow, and Prefect integrations
This will save you hours of setup and help you quickly iterate on your production-grade architecture 🏗️.
💬 Join the Community: Learn, Share, Grow
Don’t build in isolation. MLOps is evolving rapidly, and staying connected to the community is the best way to learn. Join active communities like:
- MLOps Community on Slack 🤝
- r/MachineLearning on Reddit 📢
- Weights & Biases Discord 💬
These spaces are perfect for asking questions, sharing projects, and getting feedback from practitioners, contributors, and tool creators worldwide 🌍.
📣 Your Next Steps
Here’s how you can take immediate action:
✅ Subscribe to our newsletter – Get updates on new tools, tutorials, and expert interviews delivered to your inbox every month 📰.
🖨️ Download a printable version of the MLOps Lifecycle Diagram – Hang it on your team’s wall, use it in presentations, or print it as a workflow reference cheat sheet.
🔗 Share this article with your team – Help your engineering squad align on best practices and tooling decisions. Collaboration starts with a shared foundation 🧱.
🎯 Recommended: Want a physical version of your stack map? Try Canvanizer, a digital and printable canvas tool for mapping architectures and workflows. It’s perfect for workshops, planning sessions, or sprint retros.
Thank you for diving deep into this guide 🙏. With the right stack, a small team can build machine learning systems that are scalable, robust, and budget-friendly. Bookmark this resource, refer back often, and remember—MLOps is a journey, not a checkbox ✅.
Let’s build smarter, faster, and together. 💪🚀
VIII. Bonus: Summary Table (Scannable Reference) 📋
Need a quick refresher? Below is your at-a-glance guide to the recommended open-source MLOps stack, organized by lifecycle stage, with primary tools, budget-friendly alternatives, and decision criteria tailored for startup environments.
This table is designed to help you quickly compare trade-offs and make informed tooling choices based on your team’s size, skill set, and infrastructure readiness. Whether you’re just getting started or iterating on your current stack, keep this reference handy 🧠.
| MLOps Stage | Primary Tool | Budget-Friendly Alternative | Key Startup Considerations |
| 📦 Data & Model Versioning | DVC | Git LFS, lakeFS | Git-like workflow for extensive data; DVC adds pipelines and metrics tracking 🧬 |
| 📊 Experiment Tracking | MLflow | Weights & Biases (Free), Neptune.ai | Trade-off between self-hosting vs feature-rich UIs; MLflow great for complete control ⚖️ |
| 🔁 Orchestration | Prefect | Airflow, Kubeflow Pipelines | Prefect = Python-native + modern UI; Airflow = mature + steep learning curve 🧠 |
| 🚀 Model Serving | BentoML | Seldon Core | BentoML = developer-friendly microservices; Seldon = scalable, but K8s expertise needed ⚙️ |
| 🔍 Monitoring | Evidently AI | Prometheus + Grafana | Evidently = built for ML drift; Prometheus = powerful, general-purpose + more setup 🧪 |
| ⚙️ CI/CD for ML | CML | GitHub Actions | CML adds ML-native steps into Git workflows; GitHub Actions = easy start, extensible 🔧 |
💡 Printable Version Available: Would you like to stick this to your whiteboard or pin it in Slack? Download the printable PDF version of this table here — formatted for both A4 and Letter paper sizes. It’s perfect for team onboarding, architecture reviews, or sprint planning sessions 🗂️.
🎯 Recommended: For teams planning their stack visually, try using Miro—a collaborative whiteboarding tool that’s perfect for mapping MLOps workflows, dependencies, and integration strategies. It’s used by companies like Cisco and Dell, and its free plan is excellent for early-stage teams 🌐.
✅ With this summary in hand, you now have a complete blueprint for building a cost-effective, modular, and robust open-source MLOps stack in 2025. Refer to it often, share it with your team, and continue leveling up with the in-depth related articles 🔗.
Ready to build? Let’s make your ML systems faster, cheaper, and smarter—together 🤝.
IX. Related Articles 🔗
Ready to dive deeper into specific parts of the stack? Each of these related articles provides a comprehensive, hands-on guide for a key tool or decision point in your MLOps journey. Use them to move from strategy to execution, one component at a time 🧠🔧.
📦 Data & Model Versioning on a Budget
Learn how DVC, Git LFS, and lakeFS compare in terms of scalability, Git integration, and reproducibility.
👉 Read the complete guide to find the best versioning solution for your startup’s data workflows.
🔁 Choosing Your Orchestrator: Airflow vs. Kubeflow vs. Prefect
Are you unsure which orchestration tool is right for your team? We break down the pros, cons, and use cases for Apache Airflow, Kubeflow Pipelines, and Prefect.
👉 Compare tools here and make the right call for your automation layer.
📊 Lean Experiment Tracking: MLflow vs. Weights & Biases vs. Neptune.ai
We evaluate MLflow, Weights & Biases, and Neptune.ai to help you choose the most efficient way to log experiments, track models, and collaborate.
👉 Explore the feature matrix to select a tracker that scales with your needs.
🚀 Deploying Models Without Breaking the Bank: Seldon Core vs. BentoML
This guide walks you through production deployment options using Seldon Core and BentoML, including REST vs. gRPC, Kubernetes setup, and containerization workflows.
👉 Read the deployment blueprint to launch your ML models quickly and securely.
🔍 Free & Open-Source Model Monitoring
Learn how to implement model monitoring with Evidently AI, Prometheus, and Grafana, including drift detection, latency tracking, and real-time alerting.
👉 Set up your observability stack and never miss a model failure again.
💸 The True Cost of “Free”: Hidden Infrastructure Costs of Self-Hosting MLOps
“Free” open-source tools can come with real costs. We analyze AWS infrastructure pricing, team workload, and scaling limitations.
👉 Read the full breakdown before committing to self-hosting your entire MLOps stack.
🧮 Is a Managed Platform (e.g., SageMaker) Ever Cheaper?
Sometimes AWS SageMaker or Google Vertex AI makes more sense than building everything from scratch. We explore break-even points and hybrid strategies.
👉 Read the comparative analysis to decide if managed services fit your case.
💼 Building Your MLOps Career: Essential Tools to Master for Interviews
Looking to level up or transition into MLOps? We highlight high-impact tools, common interview questions, and career advice to help you break into top roles.
👉 Access the career roadmap and position yourself for your next big opportunity.
⚙️ Automating the CI/CD Pipeline for ML with CML + GitHub Actions
Learn how to build a CI/CD workflow using CML and GitHub Actions to automate model training, evaluation, and deployment from pull requests.
👉 Follow the step-by-step tutorial to turn your ML workflows into robust pipelines.
🧭 Pro Tip: These related articles are also great resources for team training and onboarding. Share them with your developers, operations team, or data science peers to help everyone align on best practices 📘👥.
🎯 Recommended: If you want to organize all your MLOps learning paths in one place, try Notion as a central hub. With its free tier, you can track courses, bookmarks, GitHub repos, and pipeline designs collaboratively with your team 🗂️✨. That wraps up our article! You now have a modular, cost-effective MLOps roadmap backed by practical tools and expert insights. Ready to build? Let’s make machine learning truly production-ready—the startup way 💪🌍.


Pingback: Data & Model Versioning on a Budget: A Deep Dive into DVC vs. Git LFS vs. lakeFS - aivantage.space
Pingback: Choosing Your Orchestrator: A Startup’s Guide to Airflow vs. Kubeflow Pipelines vs. Prefect - aivantage.space
Pingback: Deploying Models without Breaking the Bank: A Practical Guide to Seldon Core vs. BentoML - aivantage.space
Pingback: Lean Experiment Tracking: MLflow vs. Weights & Biases (Free Tier) vs. Neptune.ai (Free Tier) - aivantage.space
Pingback: Is a Managed Platform (e.g., SageMaker) Ever Cheaper? A Break-Even Analysis for Startups - aivantage.space
Pingback: Automating the CI/CD Pipeline for ML: A Practical Workflow with CML and GitHub Actions - aivantage.space
Pingback: Building Your MLOps Career: Essential Open-Source Tools to Master for Interviews - aivantage.space