Automating the CI/CD Pipeline for ML: A Practical Workflow with CML and GitHub Actions
I. Introduction: Why CI/CD for Machine Learning Matters
In the rapidly evolving field of machine learning (ML), the adage ‘In ML, models are only as good as the last time they were tested ‘holds. This highlights the crucial role of CI/CD in ML, where models are not static entities but must be continuously tested and updated to ensure their effectiveness.
A model that performed well yesterday might degrade today due to data drift, pipeline failures, or changes in upstream dependencies. This underscores the urgent need for CI/CD in machine learning, making it not just a convenience but a necessity.
While traditional CI/CD focuses on pushing code to production quickly, CI/CD for ML involves additional complexities:
- Data versioning – ensuring reproducibility even as datasets evolve.
- Model evaluation gates – preventing underperforming models from being deployed.
- Pipeline reproducibility – allowing experiments to be re-run exactly, regardless of changes in code, data, or environment.
For readers exploring cost and tool strategies in more depth, check our Ultimate Guide to Cost-Effective Open-Source MLOps in 2025 — a comprehensive hub article linking CI/CD best practices to the broader MLOps ecosystem.
Authoritative frameworks, such as Google Cloud’s MLOps Guidelines, emphasize that ML deployment pipelines must incorporate continuous retraining, evaluation, and automated deployment to maintain business value.
Pro Tip: If you want hands-on experience, the Udacity Machine Learning DevOps Engineer Nanodegree walks you through real-world CI/CD for ML projects, including GitHub Actions integration and monitoring setups.
II. Understanding the Unique Challenges of CI/CD for ML
While the concept of CI/CD has been a staple in software engineering for decades, its application to machine learning workflows introduces a unique set of challenges. ML pipelines, with their dynamic data, evolving models, and stochastic processes, are inherently less deterministic than traditional software projects.
2.1 Data Dependencies
In traditional CI/CD, the primary dependency is code. However, in CI/CD for machine learning, data is the first-class citizen. This is particularly true in domains such as e-commerce, finance, or social media, where data drift —the phenomenon where the data used for training a model becomes less relevant over time —is a common occurrence.
This is where DVC (Data Version Control) becomes essential. DVC allows teams to track datasets, manage large files, and integrate data versioning into Git workflows, ensuring that every model can be traced back to the exact data and parameters used during training. Without such tooling, reproducibility suffers, and CI/CD pipelines can produce inconsistent results.
For a deeper breakdown, see our ‘Data Versioning Best Practices with DVC and Git-LFS’ cluster article, which explains how to integrate these tools into an automated ML pipeline.
Pro Tip: If your team stores large datasets in cloud storage, such as AWS S3 or Google Cloud Storage, pairing DVC with remote storage ensures scalability without compromising reproducibility.
2.2 Model Performance Metrics in CI/CD
Unlike traditional CI/CD pipelines, which focus on build success and code quality checks, ML pipelines must include performance-based gates. This means a deployment should be automatically blocked if the new model’s metrics — such as accuracy, F1-score, or mean squared error — fall below a predefined threshold compared to the current production model.
For example:
if new_model_accuracy < baseline_accuracy:
exit(1) # Block deployment
This metric-driven approach ensures that automated retraining does not accidentally degrade production performance — a common risk when handling live data. Tools like MLflow or SageMaker Model Monitor make it easier to integrate these gates directly into CI/CD workflows.
For cloud-native teams, the AWS SageMaker Model Monitor service can track model quality in production and trigger alerts when performance dips, complementing the automated checks in your CI/CD pipeline.
III. Core Tools for ML CI/CD Pipelines
Building a CI/CD for a machine learning workflow requires tools that go beyond traditional DevOps automation. These solutions must handle large datasets, track experiments, evaluate models, and integrate tightly with version control systems. Here’s a breakdown of the most important tools to consider.
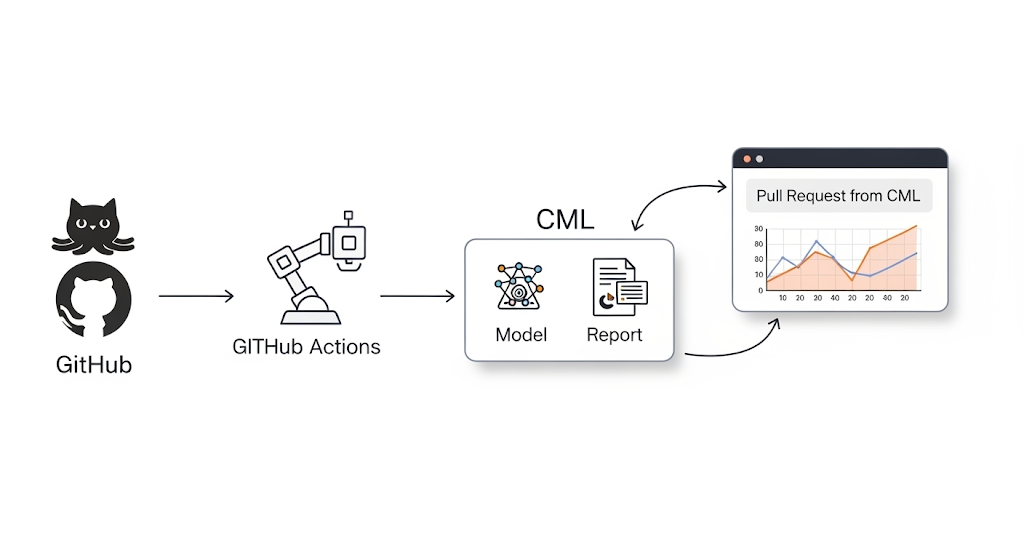
3.1 Continuous Machine Learning (CML)
CML (Continuous Machine Learning) is a specialized open-source tool designed to bring CI/CD principles into machine learning workflows. With CML, you can:
- Automate model testing every time new code or data is pushed.
- Generate metrics reports and display them directly in GitHub pull requests for fast, visual feedback.
- Integrate with cloud compute resources (AWS, GCP, Azure) to run large-scale training jobs as part of your CI/CD process.
Because it integrates directly with Git, every experiment and model update is tied to a commit — making reproducibility straightforward.
Pro Tip: Use CML in combination with DVC to ensure both code and data are versioned together, creating a fully traceable ML pipeline.
Free resource: Check out the CML Official Docs for step-by-step examples of adding automated model evaluation to your GitHub workflows.
3.2 GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions provides the automation backbone for running ML pipeline steps in response to code pushes, pull requests, or scheduled triggers. Its flexible YAML configuration allows you to define workflows that:
- Install dependencies and set up ML environments (e.g., Python, CUDA).
- Train models in cloud-hosted runners or your own self-hosted GPU instances.
- Run tests to validate data integrity, model performance, and code quality before merging.
Here’s a minimal YAML snippet to run unit tests automatically on every push:
name: CI for ML Pipeline
on: [push]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
– uses: actions/checkout@v3
– name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: 3.10
– name: Install dependencies
run: pip install -r requirements.txt
– name: Run tests
run: pytest tests/
Why it works for ML: GitHub Actions allows integration with GPU-enabled runners for training workloads and can trigger CML reports, making it a perfect hub for ML CI/CD orchestration.
3.3 Complementary Tools
While CML and GitHub Actions handle automation, you still need tools to track experiments, compare runs, and manage model registries.
One of the most popular choices is MLflow, which enables:
- Tracking of experiments and metrics across different runs.
- Storing artifacts like model binaries and evaluation reports.
- Serving trained models via REST endpoints for testing.
IV. Step-by-Step: Building a CI/CD Workflow with CML + GitHub Actions
A fully automated CI/CD pipeline for machine learning helps you version datasets, test models, monitor performance, and deploy seamlessly—all while keeping your workflow reproducible and scalable. Here’s a breakdown of each stage, with tools and examples you can apply immediately.
4.1 Setup Repository & Data Versioning
Before writing a single line of CI/CD automation, ensure your repository structure supports reproducibility. This means tracking both code and datasets in a version control system.
- Use DVC (Data Version Control) to manage datasets and ML artifacts alongside Git.
- Store large datasets remotely (e.g., AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Azure Blob) while keeping lightweight .dvc pointer files in your repository.
CLI Example:
# Initialize DVC in your repo
dvc init
# Add dataset to tracking
dvc add data/raw/dataset.csv
# Configure remote storage
dvc remote add -d myremote s3://mybucket/dvcstore
# Push dataset to remote
dvc push
By versioning datasets, your CI pipeline can reproduce exact experiments for any commit in your Git history.
4.2 Write CI Job to Train & Evaluate Model
In your GitHub Actions workflow, define a job that installs dependencies, runs your training script, and evaluates the model.
- Store the training logic in train.py and the evaluation in evaluate.py.
- Use environment variables or .env files to configure hyperparameters for different branches or environments.
Example GitHub Actions Step:
– name: Train and Evaluate Model
run: |
python train.py –epochs 10 –batch-size 32
python evaluate.py –metrics metrics.json
By running these scripts in your CI pipeline, every commit gets tested against your performance thresholds, preventing silent model degradation.
4.3 Automate Metrics Reporting in Pull Requests
Integrate CML to post model performance metrics directly into GitHub Pull Requests. This creates a fast feedback loop for data scientists and reviewers.
Example CML Command:
– name: Post CML Report
run: |
cat metrics.json >> report.md
cml comment create report.md
This automation enables stakeholders to make data-driven merge decisions without needing to review logs or artifacts.
4.4 Deployment Automation
Once the model passes all tests, trigger a deployment job to your serving infrastructure. You can use:
- Seldon Core for Kubernetes-native deployment.
- BentoML for flexible model packaging and serving.
See our in-depth comparison of Deploying Models: Seldon Core vs BentoML for a detailed examination of these options.
Example Trigger:
– name: Deploy Model
if: github.ref == ‘refs/heads/main’
run: bash deploy.sh
Recommendation:
If you want a guided, hands-on approach to building CI/CD pipelines for ML, Udemy – DevOps for Machine Learning Engineers covers GitHub Actions, Docker, and deployment best practices with practical labs.
V. Cost Considerations for CI/CD in ML
When implementing CI/CD for machine learning, it’s not just the tools that need to be considered — infrastructure costs can quickly escalate if they’re not tracked and optimized. Let’s break down the key cost drivers so you can budget wisely and avoid nasty surprises on your monthly bill.
5.1 Compute Costs for Training in CI/CD
Every time your pipeline runs a training job, it consumes compute resources. Depending on your setup, costs can vary widely:
- GitHub-hosted runners — Simple to set up, billed per minute of execution. Great for lightweight models, but costs can add up for deep learning workloads.
- Self-hosted runners — Offers more control, can be run on your cloud infrastructure (e.g., AWS EC2 Spot Instances for cost savings). This approach reduces per-minute billing from GitHub but shifts the cost to your cloud provider.
For heavy training, consider leveraging Spot Instances or scheduling jobs during off-peak hours to reduce compute costs significantly.
5.2 Storage Costs for Datasets & Artifacts
Your CI/CD pipeline doesn’t just handle code — it also needs to manage datasets, trained models, logs, and artifacts.
- AWS S3 or GCP Cloud Storage is ideal for storing large files; however, pricing tiers are crucial for effective storage management. For example, S3 Standard is fast but more expensive, whereas S3 Infrequent Access is more cost-effective for archived datasets.
- Remember: each training run may generate new model artifacts, so implement lifecycle policies to auto-delete or archive old models.
See our breakdown in The True Cost of “Free” Self-Hosted MLOps on AWS for a deeper dive into storage pricing traps and optimization strategies.
5.3 Estimating Your Total CI/CD Cost
Before committing to a specific architecture, use the AWS Pricing Calculator to forecast monthly expenses based on your expected:
- Number of training runs per day.
- Dataset size and artifact retention policy.
- Deployment frequency.
This small step can prevent budget overruns and help you compare the cost trade-offs between cloud providers or hosting strategies.
VI. Scaling CI/CD for Team Collaboration
Building a CI/CD pipeline for machine learning that works for a single developer is one thing — scaling it for a whole data science and engineering team is an entirely different challenge. When multiple contributors are pushing code, training models, and deploying to production, well-structured collaboration practices become essential.
6.1 Multi-Environment Testing
Just like in traditional software engineering, separating staging and production environments is critical for ML pipelines.
- Staging environments allow teams to test new models against real-world datasets without risking production stability.
- Production environments should only receive models that pass performance gates (e.g., accuracy above the target threshold, with no data drift detected).
You can implement environment separation using GitHub Actions environment protection rules or tools like AWS CodePipeline to manage automated deployments.
6.2 Branch-Based Deployment Triggers
One of the most effective collaboration strategies is to tie model deployments to Git branches:
- Feature branches — Ideal for experimenting with new model architectures or hyperparameter tuning.
- Main branch — Reserved for stable, production-ready models.
By integrating branch-based triggers into your CI/CD workflow, you can deploy experimental models to a test endpoint (e.g., via Seldon Core or BentoML) without disrupting production.
Related reading: See our detailed comparison in Deploying Models: Seldon Core vs BentoML for the pros and cons of each serving framework.
6.3 Role of Review Apps
Review apps (also known as preview deployments) provide stakeholders and QA engineers with a working version of the model or API before it goes live.
- For ML teams, this could mean spinning up a temporary inference API with the new model for product managers or data analysts to test.
- Popular platforms like Heroku Review Apps or Vercel Preview Deployments can be adapted for ML services with some configuration.
For cloud-native ML deployments, AWS Elastic Beanstalk can be set up to automatically spin up review environments from pull requests.
VII. Best Practices for ML CI/CD Workflows
Designing a robust CI/CD for a machine learning pipeline isn’t just about automating builds and deployments — it’s about ensuring speed, reproducibility, and model quality over time. Implementing proper best practices will help you avoid common pitfalls, such as long build times, inconsistent results, and undetected model drift.
7.1 Use Caching to Speed Up Builds
Training ML models in CI/CD workflows can be computationally expensive. By implementing caching strategies, you can drastically reduce pipeline run times:
- Cache preprocessed datasets to skip repetitive ETL steps.
- Store intermediate model artifacts so retraining can resume from checkpoints instead of starting from scratch.
- In GitHub Actions, use the’ actions/cache’ action to persist dependencies and data between workflow runs.
If your workloads run on AWS, Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) can be mounted across builds for persistent, shared storage.
7.2 Include Reproducibility in Pipeline Design
In ML, reproducibility is non-negotiable — a model that works today but can’t be replicated tomorrow is a liability.
- Version your datasets using tools like DVC.
- Log hyperparameters, metrics, and code snapshots with MLflow or similar tools.
- Lock dependencies in a requirements.txt or poetry.lock file to ensure identical environments.
This not only satisfies audit and compliance requirements but also builds trust with engineering peers and hiring managers in technical interviews.
7.3 Automate Drift Detection Integration
Model performance doesn’t degrade overnight — it’s a slow decline caused by data drift and concept drift. Embedding drift detection into your CI/CD workflow ensures that new deployments are validated against the realities of production data.
- Run periodic drift checks with Evidently AI.
- Trigger alerts or rollback workflows if drift exceeds thresholds.
- Utilize monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana for visualization and alerting purposes.
Related reading: Free & Open-Source Model Monitoring: Evidently AI with Prometheus & Grafana — a complete guide to implementing a zero-cost monitoring stack.
VIII. Common Interview Questions on CI/CD for ML
If you’re preparing for MLOps interviews, expect questions that go beyond basic DevOps knowledge. Recruiters and hiring managers want to see a practical understanding of the unique challenges in CI/CD for machine learning. Below are some frequently asked questions, along with guidance on how to approach them for maximum impact.
8.1 “How would you implement CI/CD for ML models?”
Here, the interviewer is looking for structured thinking and familiarity with the end-to-end ML workflow.
A strong answer would:
- Mention data versioning with tools like DVC.
- Explain automated model testing and evaluation using CML and GitHub Actions.
- Discuss deployment automation with serving frameworks like Seldon Core or BentoML.
- Highlight integration with monitoring solutions to catch regressions post-deployment.
Pro Tip: Reference your own GitHub repo with an example CI/CD ML pipeline — it adds credibility and can become a talking point in the interview.
8.2 “What’s the difference between CI/CD for ML vs traditional software?”
Interviewers want to know if you understand why ML introduces extra complexity:
- Data dependencies: ML workflows rely on large, evolving datasets, unlike static codebases.
- Model evaluation metrics: Deployments are often gated by metrics like F1 score or RMSE, not just unit tests.
- Reproducibility requirements: Identical environments, dataset versions, and dependencies are critical to ensure the model behaves as expected.
For a deeper dive, see Google Cloud’s MLOps Guidelines.
8.3 “How do you ensure reproducibility in ML pipelines?”
This is a favorite technical question because reproducibility is where many ML teams fail. Your answer should touch on:
- Version-controlling datasets and artifacts with DVC or Git-LFS.
- Logging experiments with MLflow or Weights & Biases.
- Using containerization (Docker) for consistent environments.
- Freezing dependencies in requirements files or Conda environments.
Related: Building Your MLOps Career: Essential Open-Source Tools to Master for Interviews — covers must-know tools for MLOps interviews.
IX. FAQ – Voice Search Optimized
When optimizing CI/CD for machine learning, it’s essential to target the exact phrasing people use in voice search. Below are two highly searched Q&As tailored for conversational queries.
Q: “What is the best CI/CD tool for machine learning?”
If you’re building open-source MLOps pipelines, CML (Continuous Machine Learning) paired with GitHub Actions is an excellent choice. This combo lets you run training, evaluation, and deployment automation directly from pull requests, making it easy for distributed teams to collaborate.
For AWS-centric teams, SageMaker Pipelines is a strong alternative. It’s fully managed, integrates natively with AWS services like S3 and CloudWatch, and helps enforce compliance for enterprise workloads.
Recommendation: If you want to go deep into SageMaker workflows, consider the Udacity – Machine Learning DevOps Engineer Nanodegree — it covers CI/CD integrations extensively.
Q: “Can I run CI/CD for ML on free tiers?”
Yes — you can start on GitHub Actions’ free tier or GitLab CI/CD at no cost for smaller workloads. However, training-heavy jobs can quickly exhaust free build minutes.
Two tips to stretch your budget:
- Use self-hosted runners for compute-intensive tasks — this allows you to connect on-premises or cloud servers to avoid usage caps.
- Adopt data versioning with DVC to avoid re-uploading massive datasets every run, reducing both storage and network costs.
For AWS-heavy teams, you can also use AWS Free Tier with small EC2 instances to host your runners and reduce monthly expenses.
X. Recommended Learning Resources
Whether you’re an aspiring MLOps engineer or a seasoned developer leveling up your automation skills, these resources will accelerate your CI/CD mastery.
- Recommendation: Udacity – Machine Learning DevOps Engineer Nanodegree — deep dive into MLflow, CML, GitHub Actions, and Kubernetes.
- Recommendation: Exponent – MLOps & System Design Interview Prep — ideal for acing ML CI/CD interview questions and whiteboard challenges.
- Free: GitHub Actions Documentation — official guide to building automation workflows.
Free: CML Docs — learn how to integrate ML training and evaluation into CI/CD pipelines.